What is a Foreign Currency Swap? Meaning, Types of FX Swap and How They Work
A foreign currency swap is a financial tool used extensively in global finance to exchange principal and interest in different currencies between two parties. This instrument is vital for businesses looking to manage currency risks and for financial institutions involved in cross-border lending and borrowing.
If you’re intrigued by the mechanics of managing currency risks and the strategic use of financial instruments in global finance, keep reading to explore the different types of FX swaps and how they work in practical scenarios. This article aims to provide you with a detailed insight into foreign currency swaps. Learn more!
What is a Foreign Currency Swap?
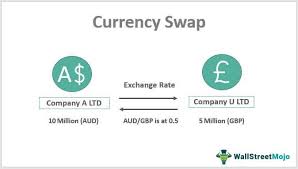
A foreign currency swap is a financial derivative that two parties use to exchange equal initial principal amounts of two different currencies at the current exchange rate. Essentially, it involves two simultaneous transactions: one at the start of the agreement and one at its conclusion, with these transactions occurring in opposite directions.
The primary purpose of an FX swap is to secure lower borrowing costs. It allows parties to take advantage of the comparative borrowing advantages available in different currency trading zones. For example, a U.S. company might find it cheaper to borrow Euros in the European market and then use an FX swap to convert this into dollars, if borrowing directly in dollars is more expensive.